Top 10 Business Automation Tools That Saved Me 100+ Hours in 2025

Business automation has evolved from a luxury for large enterprises to an essential survival strategy for businesses of all sizes. In 2025, the companies that thrive are those that have successfully automated their routine processes, freeing human talent to focus on strategic initiatives that drive growth and innovation.
After implementing automation systems across dozens of businesses and testing over 30 automation platforms, I've discovered that successful automation isn't about replacing humans with technology—it's about creating intelligent systems that amplify human capabilities while eliminating the mundane tasks that drain productivity and stifle growth.
The automation landscape has fundamentally shifted in 2025. No-code platforms have democratized automation, making sophisticated workflow orchestration accessible to non-technical users. Artificial intelligence has enhanced automation capabilities, enabling systems to handle complex decision-making that previously required human intervention. Integration capabilities have expanded dramatically, allowing seamless connections between virtually any business applications.
This comprehensive guide reveals the proven automation strategies, tools, and implementation frameworks that separate automation success stories from expensive failures. Whether you're automating your first process or scaling existing automation initiatives, these battle-tested insights will help you build systems that deliver measurable ROI while positioning your business for sustainable growth.
The businesses that master automation in 2025 will enjoy competitive advantages that compound over time: lower operational costs, faster execution speeds, improved accuracy, and the ability to scale operations without proportional increases in overhead. More importantly, they'll free their teams to focus on the creative, strategic, and relationship-building activities that truly differentiate successful businesses in an increasingly automated world.
Automation Fundamentals: Building Your Foundation for Success

Understanding automation fundamentals is crucial for avoiding the common pitfalls that lead to failed implementations and wasted investments. Successful automation requires strategic thinking about which processes to automate, in what order, and with what expected outcomes.
What to Automate First: The Strategic Priority Framework
The most successful automation initiatives begin with high-impact, low-complexity processes that deliver quick wins while building organizational confidence in automation capabilities. This strategic approach creates momentum for more ambitious automation projects while demonstrating clear value to stakeholders.
High-Frequency, Low-Complexity Tasks represent the ideal starting point for automation initiatives. These processes occur regularly, follow predictable patterns, and require minimal decision-making complexity. Examples include data entry, report generation, email responses, and routine administrative tasks. Automating these processes typically delivers immediate time savings and ROI that justifies further automation investments.
Rule-Based Decision Processes offer excellent automation opportunities because they follow logical frameworks that can be systematically programmed. Invoice approval workflows, customer service routing, inventory management, and quality control processes often fall into this category. These automations reduce human error while ensuring consistent application of business rules.
Data Movement and Integration Tasks consume significant time in most organizations but offer straightforward automation opportunities. Synchronizing data between systems, generating reports from multiple sources, and maintaining database consistency are prime candidates for automation that deliver both time savings and improved accuracy.
ROI Calculation Framework: Measuring Automation Success
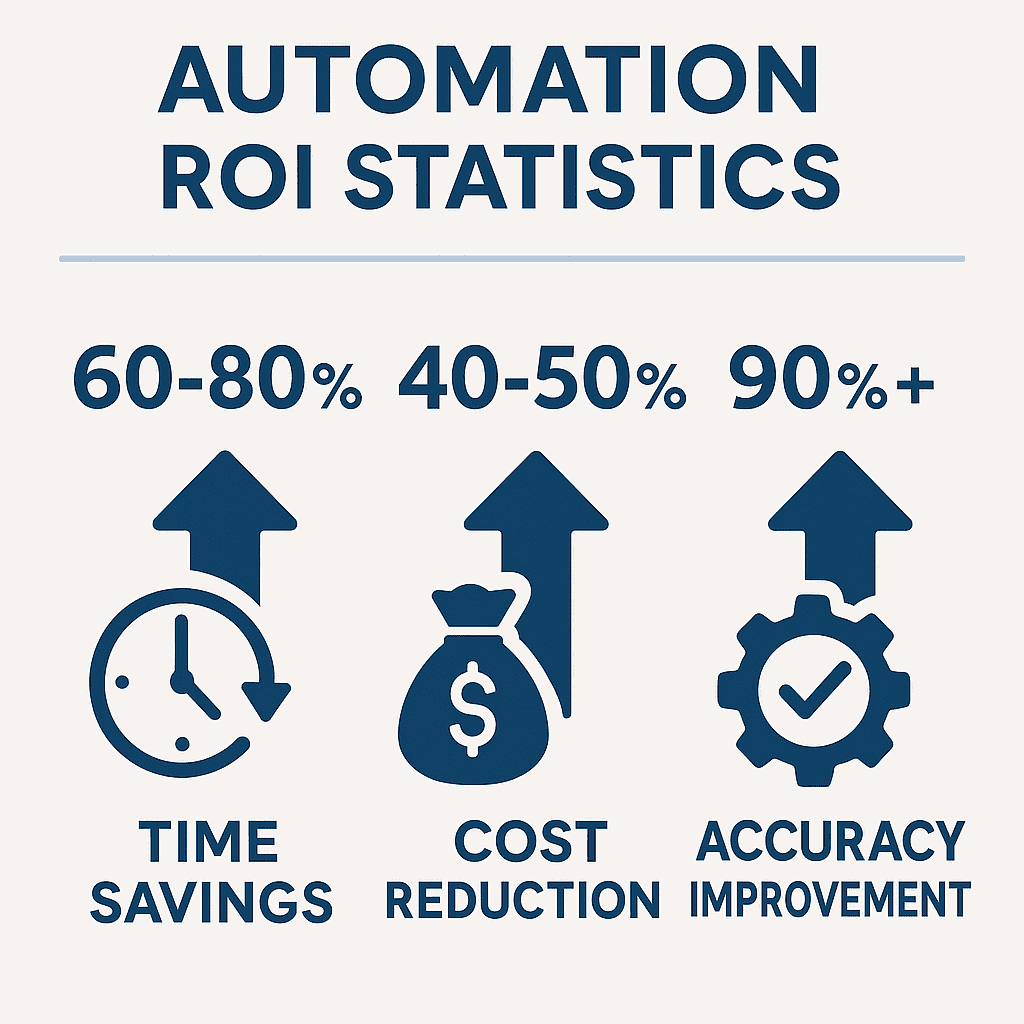
Effective automation requires clear metrics for measuring success and justifying continued investment. The most comprehensive ROI analysis considers both quantitative benefits like time savings and cost reduction, as well as qualitative improvements like accuracy enhancement and employee satisfaction.
Direct Cost Savings represent the most measurable automation benefits. Calculate the hourly cost of manual processes, including salary, benefits, and overhead, then multiply by the time saved through automation. For example, if automation eliminates 10 hours weekly of 25/hourwork,theannualsavingsexceed25/hour work, the annual savings exceed 25/hourwork,theannualsavingsexceed13,000 before considering additional benefits [1].
Indirect Benefits often provide greater value than direct cost savings but require more sophisticated measurement approaches. Improved accuracy reduces error correction costs, faster processing enables better customer service, and consistent execution enhances quality control. These benefits compound over time and often justify automation investments even when direct savings are modest.
Implementation Costs must include not only software licensing but also setup time, training requirements, and ongoing maintenance. Successful automation projects typically achieve positive ROI within 6-12 months, with benefits accelerating as systems mature and additional processes are automated.
Common Automation Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Learning from common automation failures can save significant time and resources while increasing the likelihood of successful implementations. The most frequent mistakes involve automating the wrong processes, choosing inappropriate tools, or failing to prepare organizations for automation changes.
Automating Broken Processes represents the most expensive automation mistake. If a manual process is inefficient, confusing, or poorly designed, automation will simply execute bad processes faster. Always optimize processes before automating them, ensuring that automated workflows reflect best practices rather than historical inefficiencies.
Over-Engineering Solutions occurs when organizations choose complex automation platforms for simple tasks or attempt to automate every possible variation of a process. Start with simple automations that address the most common scenarios, then gradually add complexity as systems prove reliable and valuable.
Insufficient Change Management causes many technically successful automations to fail in practice. Employees may resist automated systems, continue using manual processes, or fail to maintain automated workflows properly. Successful automation requires training, communication, and organizational commitment to new processes.
Vendor Lock-in and Integration Limitations can create long-term problems even when initial automation implementations succeed. Choose automation platforms that offer strong integration capabilities, data export options, and flexibility to adapt as business needs evolve.
Building Automation Readiness
Organizational readiness significantly impacts automation success rates. Companies that invest in automation foundations—including data quality, process documentation, and technical infrastructure—achieve better results with lower implementation costs and faster time-to-value.
Data Quality and Standardization forms the foundation of effective automation. Automated systems require clean, consistent data to operate reliably. Invest in data cleaning, standardization, and quality control processes before implementing automation that depends on data accuracy.
Process Documentation and Standardization enables more effective automation design and implementation. Document current processes, identify variations and exceptions, and standardize approaches before attempting automation. This preparation reduces implementation complexity while improving automation reliability.
Technical Infrastructure Assessment ensures that automation platforms can integrate effectively with existing systems. Evaluate API availability, data formats, security requirements, and performance capabilities before selecting automation tools. Infrastructure limitations often become expensive bottlenecks after automation implementation begins.
Team Skills and Training requirements vary significantly across automation platforms. No-code tools enable broader participation in automation development, while more sophisticated platforms may require technical expertise. Assess current team capabilities and plan training or hiring accordingly.
Essential Automation Categories: Transforming Core Business Functions
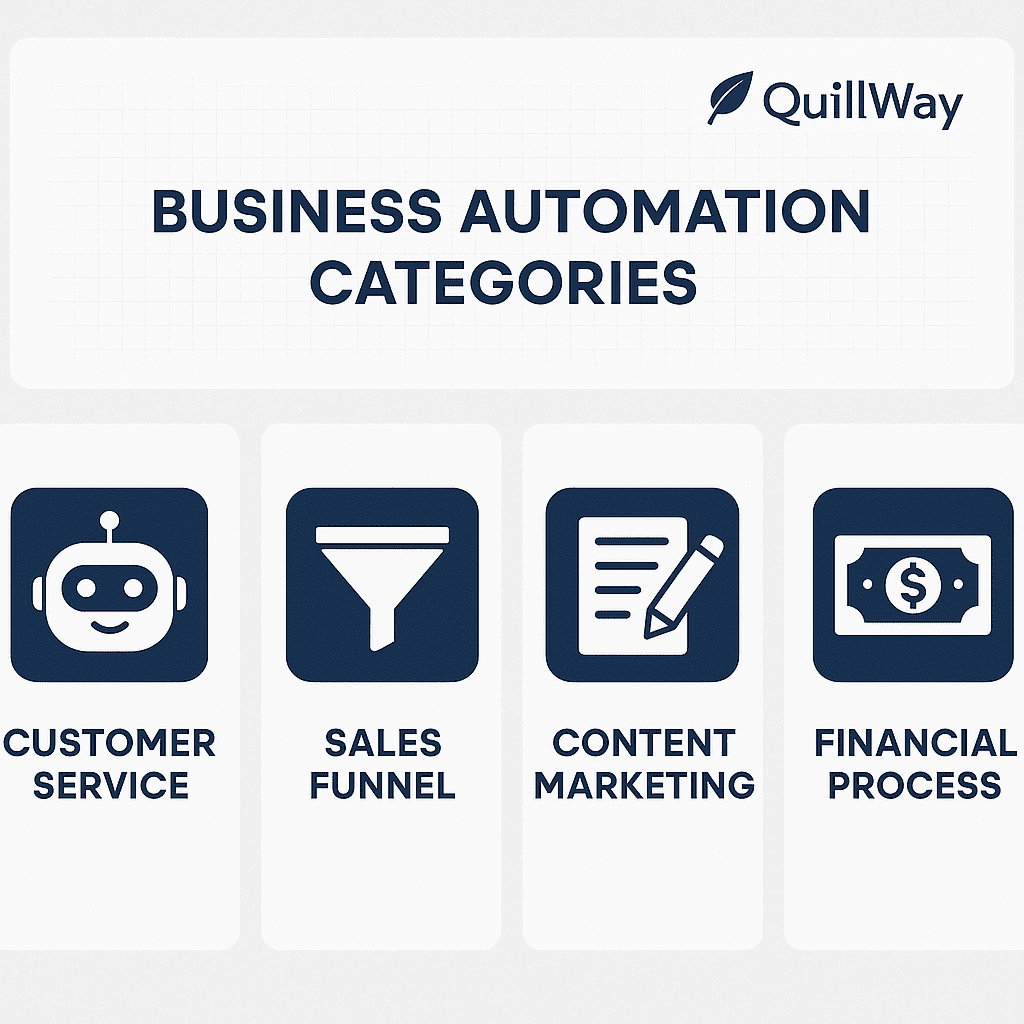
Modern businesses operate across multiple functional areas that each offer distinct automation opportunities. Understanding the unique characteristics, challenges, and benefits of automating different business functions enables more strategic automation planning and implementation.
Customer Service Automation: Enhancing Experience While Reducing Costs
Customer service automation has evolved far beyond simple chatbots to encompass sophisticated systems that can handle complex inquiries, route requests intelligently, and provide personalized support experiences. The most effective customer service automation enhances rather than replaces human interaction, handling routine inquiries while escalating complex issues to human agents.
Intelligent Chatbot Implementation represents the foundation of modern customer service automation. Advanced chatbots powered by natural language processing can understand customer intent, access knowledge bases, and provide accurate responses to common inquiries. The key is designing chatbot interactions that feel natural while efficiently resolving customer needs.
Modern chatbots can handle account inquiries, order status updates, basic troubleshooting, and information requests without human intervention. When implemented effectively, chatbots resolve 70-80% of routine inquiries while providing 24/7 availability that improves customer satisfaction [2]. The most successful implementations include clear escalation paths to human agents when chatbot capabilities are exceeded.
Automated Ticket Routing and Prioritization ensures that customer inquiries reach the most appropriate support agents based on issue type, customer priority, and agent expertise. This automation reduces response times while improving resolution quality by matching inquiries with agents who have relevant knowledge and experience.
Sophisticated routing systems consider multiple factors including customer tier, issue complexity, agent workload, and historical resolution patterns. This intelligent routing can reduce average resolution time by 40-50% while improving customer satisfaction through more effective issue matching [3].
Knowledge Base Automation and Maintenance keeps support resources current and accessible while reducing the burden on support agents to answer repetitive questions. Automated systems can identify common inquiry patterns, suggest knowledge base updates, and even generate initial article drafts based on successful support interactions.
Self-Service Portal Enhancement empowers customers to resolve issues independently while reducing support ticket volume. Automated systems can guide customers through troubleshooting processes, provide personalized recommendations, and escalate to human support when self-service options are insufficient.
Sales Funnel Automation: Optimizing Revenue Generation
Sales funnel automation encompasses the systematic optimization of every stage in the customer acquisition and conversion process. From initial lead capture through final purchase and beyond, automation can improve conversion rates while reducing the manual effort required to manage prospects and customers.
Lead Capture and Qualification Automation ensures that potential customers are identified, categorized, and nurtured appropriately based on their characteristics and behavior. Automated lead scoring systems evaluate prospects based on demographic information, engagement patterns, and behavioral indicators to prioritize sales efforts on the most promising opportunities.
Modern lead qualification systems can analyze website behavior, email engagement, social media activity, and demographic data to create comprehensive prospect profiles. This automation enables sales teams to focus their limited time on prospects with the highest conversion probability while ensuring that lower-priority leads receive appropriate nurturing.
Email Marketing Automation and Personalization delivers targeted messages based on prospect behavior, preferences, and position in the sales funnel. Sophisticated email automation can trigger personalized sequences based on specific actions, segment audiences for targeted messaging, and optimize send times for maximum engagement.
Effective email automation goes beyond simple autoresponders to include behavioral triggers, dynamic content personalization, and intelligent send-time optimization. These systems can increase email engagement rates by 50-100% while reducing the manual effort required to maintain consistent communication with prospects [4].
Sales Process Automation and CRM Integration streamlines the administrative aspects of sales management while ensuring that opportunities are tracked and managed systematically. Automated systems can update contact records, schedule follow-up activities, generate proposals, and track sales performance metrics without manual data entry.
Customer Onboarding and Retention Automation ensures that new customers receive consistent, high-quality introduction experiences while identifying opportunities for upselling and cross-selling. Automated onboarding sequences can deliver training materials, schedule check-in calls, and monitor customer engagement to identify potential issues before they become problems.
Content Marketing Automation: Scaling Creative Output
Content marketing automation enables businesses to maintain consistent, high-quality content production while optimizing distribution and engagement across multiple channels. The most effective content automation enhances human creativity rather than replacing it, handling routine tasks while enabling content creators to focus on strategy and high-value creative work.
Content Creation and Curation Automation assists with research, ideation, and initial content development while maintaining quality standards and brand consistency. AI-powered tools can generate content outlines, suggest topics based on trending keywords, and even create initial drafts that human creators can refine and enhance.
Modern content automation tools can analyze audience engagement patterns, identify trending topics, and suggest content opportunities that align with business objectives. This automation reduces the time required for content planning while ensuring that content strategies remain data-driven and audience-focused.
Social Media Scheduling and Optimization ensures consistent social media presence while optimizing posting times and content formats for maximum engagement. Automated systems can schedule posts across multiple platforms, adapt content formats for different social networks, and analyze performance to optimize future posting strategies.
SEO and Content Optimization Automation helps content creators optimize their work for search engines while maintaining readability and value for human audiences. Automated tools can suggest keywords, analyze content structure, and recommend improvements that enhance search visibility without compromising content quality.
Content Distribution and Syndication amplifies content reach by automatically sharing content across multiple channels and platforms. This includes email newsletter distribution, social media posting, and syndication to relevant industry publications or partner websites.
Financial Process Automation: Improving Accuracy and Efficiency
Financial process automation reduces errors, improves compliance, and frees finance teams to focus on analysis and strategic planning rather than routine data processing. The high accuracy requirements and regulatory compliance needs in financial processes make automation particularly valuable for reducing risk while improving efficiency.
Invoice Processing and Accounts Payable Automation eliminates manual data entry while ensuring accurate processing and timely payments. Automated systems can extract data from invoices, match them with purchase orders, route approvals based on business rules, and schedule payments according to cash flow optimization strategies.
Modern invoice automation can handle various invoice formats, validate data accuracy, and flag exceptions for human review. This automation typically reduces invoice processing time by 60-80% while improving accuracy and reducing late payment penalties [5].
Expense Management and Reporting Automation streamlines expense submission, approval, and reimbursement processes while ensuring compliance with company policies. Automated systems can capture receipt data, categorize expenses, route approvals, and generate reports for accounting and tax purposes.
Financial Reporting and Analysis Automation generates regular financial reports while identifying trends and anomalies that require management attention. Automated reporting systems can consolidate data from multiple sources, apply consistent formatting, and distribute reports to relevant stakeholders on predetermined schedules.
Cash Flow Management and Forecasting automation helps businesses optimize working capital while predicting future cash needs. Automated systems can analyze payment patterns, predict collection timing, and recommend cash management strategies based on historical data and current trends.
Compliance and Audit Trail Automation ensures that financial processes maintain appropriate documentation and controls while reducing the manual effort required for compliance reporting. Automated systems can track all financial transactions, maintain audit trails, and generate compliance reports that meet regulatory requirements.
Tool Recommendations by Category: Choosing the Right Automation Platform
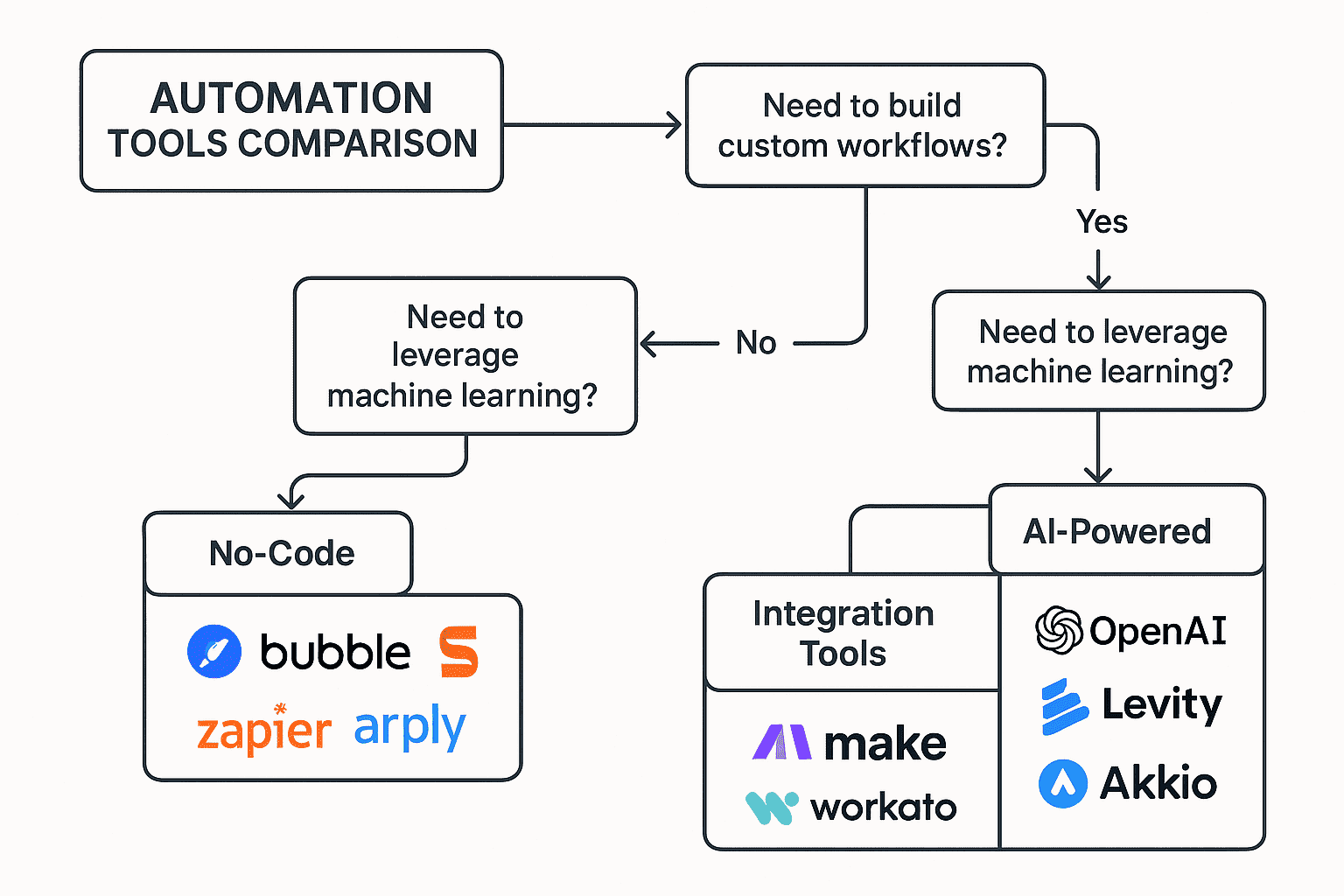
Selecting appropriate automation tools significantly impacts implementation success and long-term value. The most effective approach involves matching tool capabilities with specific business needs while considering factors like ease of use, integration capabilities, and scalability requirements.
No-Code Automation Platforms: Democratizing Automation
No-code automation platforms enable non-technical users to build sophisticated workflows without programming knowledge. These tools have revolutionized business automation by making advanced capabilities accessible to domain experts who understand business processes but lack technical skills.
Zapier remains the most popular no-code automation platform, offering connections to over 8,000 applications with an intuitive interface that enables quick automation development. Zapier excels at simple trigger-action automations and multi-step workflows that connect different business applications. The platform's strength lies in its extensive integration library and user-friendly design, making it ideal for small to medium businesses seeking quick automation wins.
Make (formerly Integromat) provides more sophisticated automation capabilities with visual workflow design and advanced logic features. Make offers better value for complex automations while maintaining accessibility for non-technical users. The platform excels at data transformation, conditional logic, and multi-branch workflows that require more sophisticated decision-making.
Microsoft Power Automate integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365 and other Microsoft products while offering enterprise-grade security and compliance features. Power Automate is particularly valuable for organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem, providing deep integration with Office applications, SharePoint, and Dynamics 365.
AI-Powered Automation Tools: Intelligent Process Enhancement
Artificial intelligence has enhanced automation capabilities by enabling systems to handle complex decision-making, natural language processing, and pattern recognition that previously required human intervention.
UiPath leads the robotic process automation (RPA) market with sophisticated AI capabilities that can automate complex desktop applications and legacy systems. UiPath excels at automating processes that involve multiple applications, complex decision trees, and exception handling. The platform is particularly valuable for large enterprises with complex IT environments.
Automation Anywhere combines RPA with AI capabilities to create intelligent automation solutions that can learn and adapt over time. The platform offers strong analytics and process discovery features that help organizations identify automation opportunities and measure results.
Blue Prism provides enterprise-grade RPA with strong governance and security features. Blue Prism is particularly well-suited for highly regulated industries that require strict compliance and audit capabilities.
Integration and Workflow Tools: Connecting Business Systems
Modern businesses rely on multiple software applications that must work together seamlessly. Integration platforms enable data flow and process coordination across different systems without requiring custom development.
MuleSoft provides enterprise-grade integration capabilities that can connect virtually any system or application. MuleSoft excels at complex integration scenarios involving legacy systems, real-time data synchronization, and high-volume transaction processing.
Workato combines integration and automation capabilities in a single platform that's accessible to both technical and business users. Workato offers pre-built connectors for popular business applications while providing the flexibility to handle custom integration requirements.
Tray.io focuses on API-first integration with visual workflow design that enables rapid development of complex integration scenarios. Tray.io is particularly strong for organizations that need to integrate modern cloud applications with sophisticated data transformation requirements.
Cost-Benefit Analysis Framework
Evaluating automation tools requires comprehensive analysis that considers both direct costs and indirect benefits. The most effective evaluation framework examines total cost of ownership, implementation complexity, and long-term value potential.
Licensing and Subscription Costs vary significantly across automation platforms, with pricing models based on factors like number of automations, data volume, or user count. Consider not only current needs but also projected growth when evaluating pricing structures.
Implementation and Training Costs can significantly impact total cost of ownership, particularly for complex platforms that require specialized skills. Factor in time required for setup, training, and initial automation development when comparing options.
Maintenance and Support Requirements affect long-term costs and success rates. Evaluate vendor support quality, community resources, and ongoing maintenance requirements when selecting automation platforms.
Scalability and Growth Potential determine whether automation investments will continue providing value as business needs evolve. Choose platforms that can accommodate growth in automation complexity, data volume, and user requirements.
Implementation Strategy: Your Step-by-Step Automation Roadmap
Successful automation implementation requires systematic planning that balances quick wins with long-term strategic objectives. The most effective approach begins with pilot projects that demonstrate value while building organizational capabilities for more ambitious automation initiatives.
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Weeks 1-4)
Current Process Documentation forms the foundation of effective automation planning. Document existing workflows, identify pain points, and quantify the time and resources required for manual processes. This baseline assessment enables accurate ROI calculations and helps prioritize automation opportunities.
Stakeholder Alignment and Goal Setting ensures that automation initiatives support broader business objectives while securing necessary resources and support. Identify key stakeholders, understand their priorities, and establish clear success metrics that align with organizational goals.
Tool Selection and Pilot Planning involves evaluating automation platforms against specific business requirements and selecting initial automation projects that offer high probability of success. Choose pilot projects that are important enough to demonstrate value but simple enough to implement quickly.
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation (Weeks 5-12)
Initial Automation Development focuses on implementing 2-3 simple automations that address high-frequency, low-complexity processes. These pilot projects should demonstrate clear value while providing learning opportunities for the automation team.
Testing and Refinement ensures that automated processes work reliably under real-world conditions. Conduct thorough testing with realistic data volumes and edge cases, then refine automations based on testing results and user feedback.
User Training and Change Management prepares the organization to adopt automated processes effectively. Provide training on new workflows, communicate benefits clearly, and address concerns or resistance proactively.
Phase 3: Expansion and Optimization (Weeks 13-26)
Automation Portfolio Expansion builds on pilot success by implementing additional automations that address more complex processes or serve additional business functions. Use lessons learned from pilot projects to improve implementation speed and success rates.
Integration and Workflow Optimization connects individual automations into comprehensive workflows that span multiple business functions. This integration often provides greater value than individual automations by eliminating handoffs and reducing overall process complexity.
Performance Monitoring and Continuous Improvement establishes systematic approaches for measuring automation effectiveness and identifying optimization opportunities. Regular performance reviews ensure that automations continue delivering value while identifying areas for enhancement.
Advanced Automation Tactics: Next-Level Optimization
Organizations that have mastered basic automation can implement advanced tactics that provide competitive advantages through sophisticated process optimization and intelligent decision-making capabilities.
AI Integration Strategies: Enhancing Automation Intelligence
Artificial intelligence transforms automation from simple rule-based systems into intelligent platforms that can adapt to changing conditions and handle complex decision-making scenarios.
Machine Learning Integration enables automation systems to improve performance over time by learning from historical data and outcomes. ML-enhanced automations can optimize scheduling, predict maintenance needs, and adapt to changing business conditions without manual reprogramming.
Natural Language Processing allows automation systems to understand and process unstructured text data, enabling automation of processes that involve email analysis, document processing, and customer communication interpretation.
Predictive Analytics Integration helps automation systems anticipate future needs and proactively address potential issues. Predictive capabilities can optimize inventory management, schedule maintenance, and identify customer retention risks before they become problems.
Cross-Platform Automation: Breaking Down Silos
Advanced automation strategies involve coordinating processes across multiple platforms and departments to create seamless end-to-end workflows that eliminate handoffs and reduce overall process complexity.
API-First Integration Approaches enable more sophisticated automation by leveraging application programming interfaces to create deep integrations between business systems. API-based automations are more reliable and scalable than screen-scraping or email-based integration approaches.
Event-Driven Architecture creates responsive automation systems that react to business events in real-time rather than operating on predetermined schedules. Event-driven automations provide faster response times and more efficient resource utilization.
Microservices and Modular Automation breaks complex processes into smaller, reusable components that can be combined in different ways to support various business scenarios. This modular approach improves flexibility while reducing development and maintenance complexity.
Future-Proofing Your Automation Systems
Building automation systems that remain valuable as business needs evolve requires strategic thinking about technology trends, organizational changes, and market dynamics.
Cloud-Native Architecture ensures that automation systems can scale efficiently while taking advantage of cloud computing benefits like automatic updates, global availability, and pay-as-you-go pricing models.
Open Standards and Interoperability reduce vendor lock-in risks while enabling integration with future technologies. Choose automation platforms that support open standards and provide data export capabilities.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation builds organizational capabilities for ongoing automation evolution. Establish processes for identifying new automation opportunities, evaluating emerging technologies, and updating existing automations as business needs change.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I automate first in my business?
Start with high-frequency, low-complexity tasks that follow predictable patterns. Examples include data entry, email responses, report generation, and routine administrative tasks. These processes offer quick wins that demonstrate automation value while building organizational confidence for more complex projects.
How much can automation save my business?
Automation savings vary significantly based on current processes and implementation quality. Most businesses see 20-50% time savings on automated processes, with some achieving 70-80% reductions in manual effort. The key is focusing on processes that consume significant time or resources while offering clear automation opportunities.
What's the difference between RPA and workflow automation?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) focuses on automating interactions with existing software applications, often through screen scraping and user interface automation. Workflow automation typically involves API-based integration between applications with more sophisticated logic and decision-making capabilities. RPA is better for legacy systems, while workflow automation is more suitable for modern cloud applications.
How do I measure automation ROI?
Calculate automation ROI by comparing implementation costs (software, setup, training) against benefits (time savings, error reduction, improved efficiency). Include both direct savings from reduced manual effort and indirect benefits like improved accuracy and faster processing. Most successful automations achieve positive ROI within 6-12 months.
Can small businesses benefit from automation?
Small businesses often see the greatest automation benefits because they have fewer resources to waste on inefficient processes. No-code automation platforms make sophisticated automation accessible to small businesses without requiring technical expertise or large budgets. Start with simple automations and gradually expand as capabilities and confidence grow.
Building Your Automated Future
Business automation in 2025 represents a fundamental shift in how organizations operate, compete, and grow. The companies that embrace automation strategically will enjoy sustainable competitive advantages through lower costs, faster execution, and improved accuracy, while freeing their teams to focus on the creative and strategic work that drives innovation and growth.
The key to automation success lies not in the technology itself, but in the strategic thinking that guides implementation decisions. The most successful automation initiatives begin with clear understanding of business objectives, systematic evaluation of automation opportunities, and disciplined implementation that prioritizes value delivery over technological sophistication.
Remember that automation is a journey, not a destination. Start with simple processes that offer clear value, build organizational capabilities through successful implementations, and gradually expand to more complex scenarios as experience and confidence grow. The businesses that approach automation systematically and strategically will build sustainable competitive advantages that compound over time.
The future belongs to organizations that can effectively combine human creativity and strategic thinking with automated efficiency and accuracy. By implementing the strategies, tools, and frameworks outlined in this guide, you'll be well-positioned to build automation systems that drive sustainable growth while enhancing rather than replacing human capabilities.
Your automation journey begins with a single step: identifying one high-impact process that could benefit from automation and implementing a simple solution that demonstrates clear value. From that foundation, you can build the automated systems that will power your business success in 2025 and beyond.
Related Articles:
•40 Revolutionary AI Tools I Tested in 2025 (Ranked)
•Enterprise AI Tool Integration
References:
[1] Business Automation ROI Analysis – https://camunda.com/blog/2024/06/the-roi-of-automation-understanding-the-impact-on-your-business/
[2] Customer Service Automation Statistics – https://www.flowforma.com/blog/workflow-automation
[3] Automated Ticket Routing Benefits – https://www.atlassian.com/agile/project-management/workflow-automation
[4] Email Marketing Automation Performance – https://zapier.com/blog/best-ai-productivity-tools/
[5] Invoice Processing Automation Results – https://www.claromentis.com/blog/15-business-automation-software-tools-to-consider-in-2025